
DigitalBlast has established a joint research course with the University of Tokyo titled “Research on Utilization of Space Resources in Private Space Stations” to create a new economic zone based on space stations and has commenced joint research.
December 14, 2023
DigitalBlast, Inc. (Headquarters: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, CEO: Shingo Horiguchi, hereinafter referred to as DigitalBlast) is pleased to announce the establishment of a joint research course with the Graduate School of Engineering, National University Corporation, The University of Tokyo (Location: Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Dean: Yasuhiro Kato, hereinafter referred to as The University of Tokyo) titled “Research on Utilization of Space Resources in Private Space Stations.”
Background
The International Space Station (ISS) is scheduled to end operations in 2030, and around the world, led by the United States, multiple private companies are advancing the development of commercial space stations that will serve as the post-ISS. In Japan, specific movements are still undecided, but the Basic Space Plan decided by the Cabinet in June 2023 includes a policy to explore private sector needs utilizing the ISS “Kibo” Japanese Experiment Module and to consider Japan’s role in the post-ISS era.
In December 2022, DigitalBlast launched the “Commercial Space Station (CSS) Initiative” to construct a space station led by the private sector within Japan. This initiative aims to build a space station led by the private sector within Japan as a venue for future activities in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). In addition to establishing an LEO economic zone led by the private sector, this space station envisions a scenario that creates an interplanetary economic zone by enabling round trips of spacecraft between extraterrestrial bodies based on the concept of In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU), utilizing resources from Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs).
In this context, the course will advance basic research on the Moon and asteroids for the utilization of resources from NEAs in the Commercial Space Station (CSS), as well as the realization of a takeoff and landing platform, led by Professor Hideaki Miyamoto of The University of Tokyo, a leading authority on space resources research, who has spearheaded research on asteroids such as “Itokawa” returned by the explorer “Hayabusa.”
Research Content
The space station modules planned by DigitalBlast will serve as a platform for the storage and supply of resources and fuels collected from asteroids. In addition to the terrestrial recovery of space resources, the station will implement on-demand production capabilities with 3D printers, aiming to realize In-Space Manufacturing (ISM).
Professor Miyamoto, who will serve as the faculty in charge, leads domestic and international research on solar system exploration and space resources, including Mars, asteroids, and the Moon. He is also involved in the “TSUKIMI Project,” which investigates the distribution and quantity of water ice and metal resources on the lunar surface using terahertz wave sensors. He conducts research on the presence of water and minerals in space on asteroids and Mars, and works on studies related to the utilization of space resources.
Under the guidance of Professor Miyamoto, the course will conduct basic research on the Moon and asteroids for the utilization of resources from extraterrestrial bodies in the CSS, and plan and consider concepts that enable the takeoff and landing of lunar and asteroid explorers in the CSS. It aims to conduct research for the future utilization of space resources and accelerate the creation of a new economic zone in space.
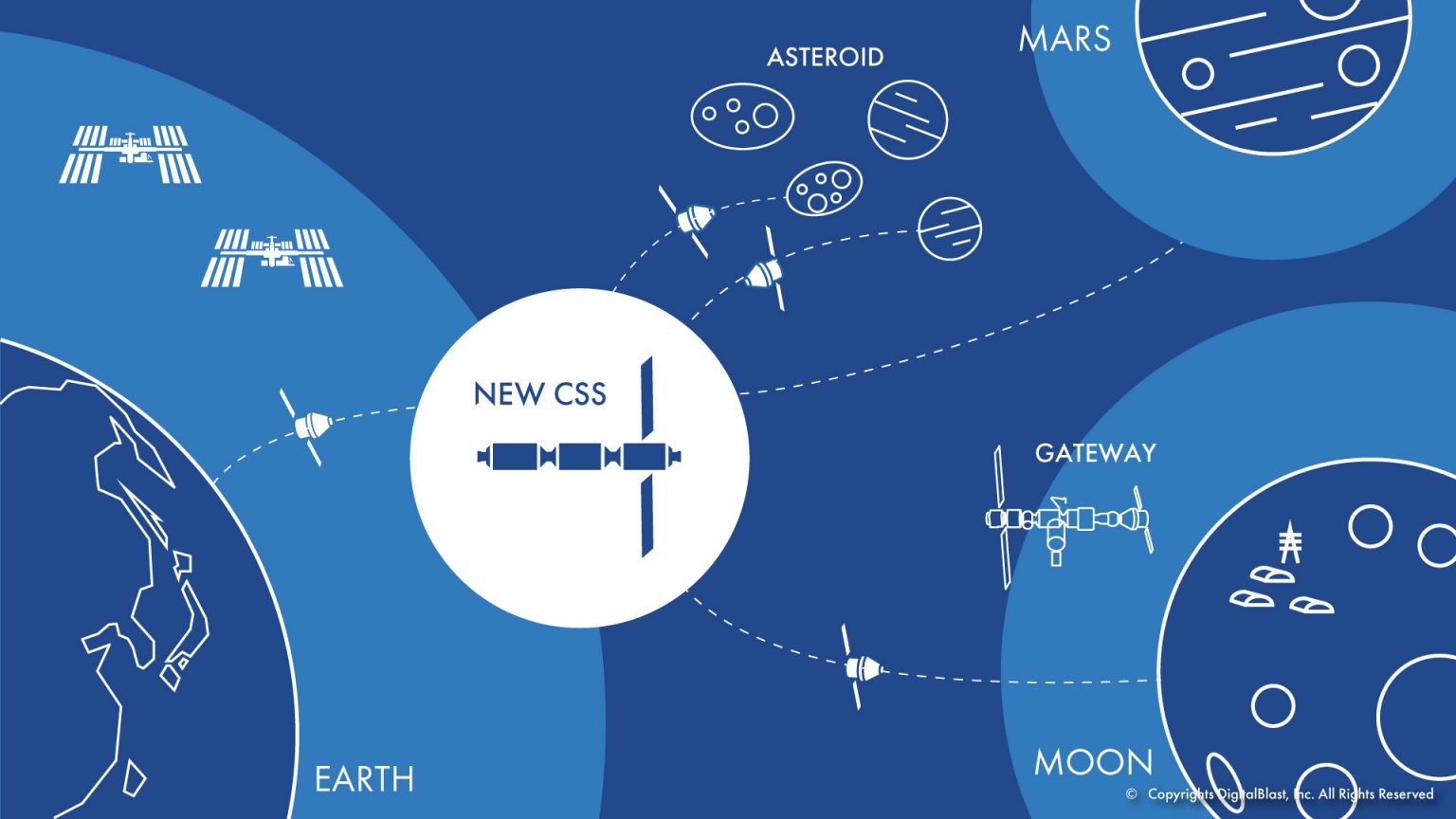
The concept of utilizing space resources based at a space station
About the Course
Course Name: Research on Utilization of Space Resources in Commercial Space Stations
Research Objective: To materialize the concept of enabling the takeoff and landing of lunar and asteroid explorers in the Commercial Space Station (CSS) for the utilization of resources from near-Earth asteroids and the Moon. To jointly conduct basic research aimed at the utilization of space resources, as well as planning and consideration of the database of lunar and asteroid resources, and calculation of market size.
Faculty in Charge: Professor Hideaki Miyamoto (Department of Systems Innovation, Graduate School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo)
Location: The University of Tokyo and DigitalBlast
Establishment & Research Period: July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2026 (3 years)
About DigitalBlast, Inc.
DigitalBlast is on a mission to redefine the value of space with its motto, “Make Space Valuable.” To enhance the worth of Japan’s space sector, it’s crucial to develop a variety of revenue streams that extend beyond BtoG (business-to-government) transactions. Boasting a diverse team skilled in business strategy, digital technology, and promotion, we take pride in our comprehensive solutions. Our goal is to expand our clients’ revenue options and forge new value within the space industry.
Company Name: DigitalBlast Inc.
Office: Jinbocho mitsui building 19F,1-105 Kanda Jinbocho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, 101-0051, Japan
Representative: Shingo Horiguchi (CEO)
Established: December 2018
Website: https://digitalblast.co.jp/
Business Content: Planning, design, and support for corporate transformation, development and support of digital technology, integrated marketing services, digital marketing services, internet advertising services, video production and distribution.


